Understanding PoC, MVP and Prototypes – Programmers Force Development Guide
Product development is a complex process as organizations must focus on different factors impacting the budget. Many companies struggle to decide on a suitable development method in this fast-paced modern landscape. The global digital transformation market was valued at $469 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at 16.5% CAGR, touching an enormous $1009.8 billion mark by 2025. Different approaches are used for strategic planning and idea evaluation, such as PoC, Prototypes, and MVP. Each method is tailored for a specific type of project and aims to provide a headstart to any startup or small-scale business looking to make a footprint in the digital world. Depending on the development environment, each approach has advantages that vary for every company at the concept, pre-seed, and seed stages.
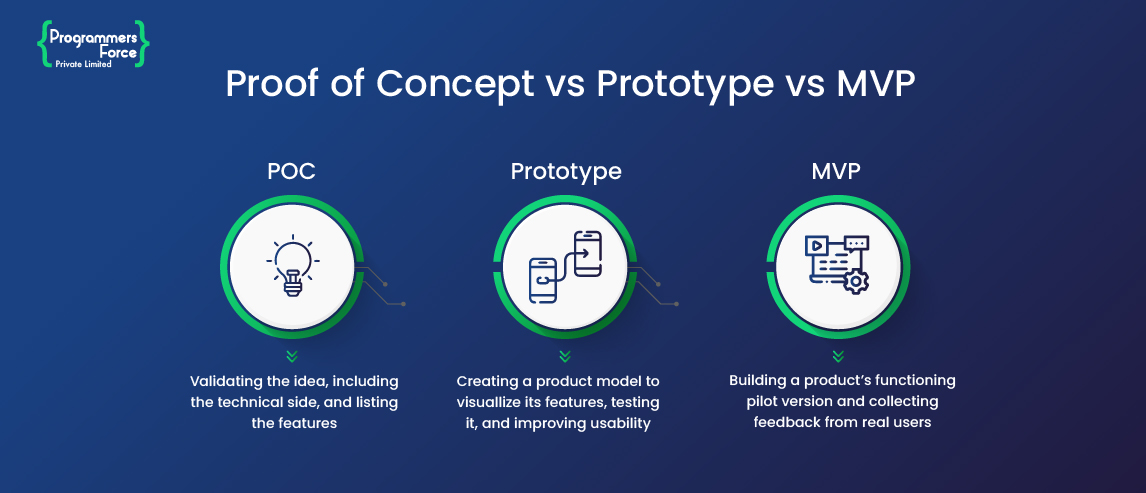
What are PoC, MVP, and Prototype?
Companies invest a tremendous amount to create good digital products that promote their services. Building innovative mobile and web-based applications require complete evaluation before idea implementation. PoC (Proof-of-Concept), Prototypes, and MVP (Minimum Viable Product) are different approaches that prove fruitful in the entire development cycle. Choosing any of these approaches before deploying a real-world digital application can save a firm time and investment. PoC, MVP, and prototypes are not different forms for creation; rather than they refer to different stages in product development. This blog covers all approaches that evaluate business ideas at every step of the development cycle.
PoC – Idea Validation
Proof of Concept (POC) is a method to validate assumptions regarding the final product by determining technical aspects keeping the end customer in mind. In the modern world, a PoC is a validation technique that provides insights into an idea and its development costs without consuming excessive time and resources. It is a small project in which teams test the technical aspects such as method, tools, and integration to be implementable. PoC enables firms to evaluate the core functionalities of the product in line with the final objective it aims to achieve. A complex idea may require multiple PoCs to assess the performance of each functionality as per requirements and budget.
Significant advantages of PoC for Startups
PoC can be helpful for investors and shareholders as it verifies the workable nature of an idea. Building a PoC requires complete vision estimation from start to finish. It helps assess the idea’s flawless nature based on the initial study.
- Companies can take advantage by generating idea feasibility reports that assure the potential. It reduces the cost and time of feature validation compared to a full-scale project.
- From PoC evaluation, the firm also gets innovative solutions to solve implementation problems.
- PoC discloses the initial bugs and risks, confirming the project’s viability which saves time and cost for the organization, enabling firms to decide on the right tools and technologies for the projects.
Prototype – Idea Visualization
A prototype is where the project enters the design phase and starts to take real-time formation. After complete technical evaluation from the PoC phase, the project undergoes prototyping to lay the foundation for the product’s look and feel, i.e., idea visualization. Prototype creation involves multiple team efforts with cross-functional interactions between designers, developers, and owners to finalize product design. Prototypes offer a complete UI approach specifying all the design elements that can improve product interaction and user experience. They are sometimes referred to as wireframes or “clickable” design versions. Mainly designed using Figma and Invision Studio, a prototype visualizes the look by which the investors can demonstrate the workflow of the end product.
Prototyping Advantages for Startups
Prototype development also has a short lifespan in the product development cycle, but it is crucial as it ensures testing, demonstration, and discussions on the end-product design. Prototypes polish the concept and move the product into development phases with complete design planning.
- Prototypes optimize the resources by identifying essential UI elements necessary for the application and removing the extra components before proceeding into the development phase.
- Prototypes are great for convincing investors to consider the product’s potential for future fundraising.
- Modern prototyping tools help create interactive designs that can improve in multiple iterations after taking feedback from the core team.
MVP – Idea Solution
After a project gets approved from the prototype phase, it moves onto the implementation part of the development cycle. This is where the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) delivers the possible solution to the idea. The MVP depends on the context of the idea and product delivery. An MVP can differ for every project; in other words, it allows a firm to measure the demand and product market fit, whether it attracts early adopters or not. A minimum viable product is a working deliverable that packs the minimum features to satisfy early customers’ feedback for future development increments. MVP differs from PoC and Prototypes as it delivers a usable product that provides user interaction.
Benefits of MVP
A minimum viable product is an excellent tool to get an initial working product deliverable. It gives firms adequate feedback and improves subsequent product revisions. The MVP presents the solution to the problems related to the finalized idea in the PoC phase.
- An MVP deliverable saves money and resources as it only features the core implementations to check the working nature of the product. Also, the user feedback analysis lays a strong foundation for developers on future product revisions.
- An excellent functional MVP attracts more potential investors resulting in a significant rise in product budget.
- With an MVP out on the market, the development team can acquire more users to support the future development plan.
Final Thoughts
Proof of Concept, Prototype, and MVP facilitate product development through each working cycle. They provide a practical blueprint for every organization to work on their new ideas. PoC proposes a feasible solution for business ideas, while a prototype creates a visual representation of the product that goes into development after feedback from owners and stakeholders. The minimum viable product defines the working foundations and is used for beta testing and investor satisfaction. MVP provides a basic working model within the defined budget that can be improved in the future. Each part is vital to create a fully-functional end product that benefits organizations.